December 10, 2025
Knee pain – Cartilage Injury of the knee
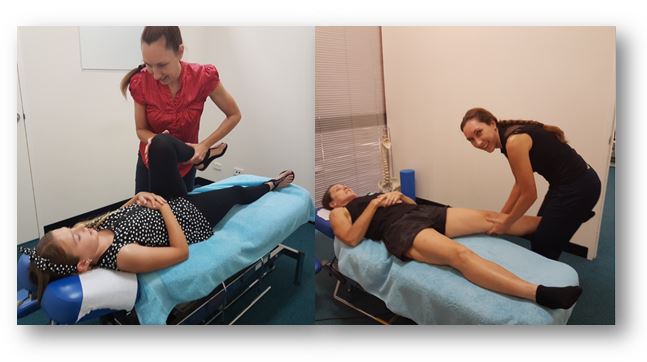
Knee cartilage injury (Meniscal) is one of the most common type of knee injuries encountered. Meniscal injury is the tear of the knee cartilage, a fibrous cartilage structure that is located between the femur (thigh bone) and the tibia (lower leg) in the knee joint. The meniscus/cartilage of the knee acts as a shock absorber during body movement and activities as well as cushioning the joint to ensure the articular surfaces of the femur and tibia are undamaged and healthy. It is most commonly found in athletes, especially those who participate in contact sports such as rugby. Knee cartilage injury can also occur in elderly as the cartilage might degenerate due to knee joint arthritis.
What causes Knee cartilage meniscal injury?
The knee cartilage is most susceptible to tearing during activities that involves twisting of the knee when it is slightly bent or flexed. One example as such activity may be when a person twisted his or her knee while squatting. The meniscus is generally weakened in the elderly, therefore, simple actions such as having an awkward twist while standing up from the chair might result in a tear on the cartilage.
Symptoms of cartilage/meniscal injury
In most cases, when the meniscus is torn, patients can feel a “pop” in the knee and still being able to walk with the injured knee. However, after a few days, their knee might get swollen and stiff, sometimes accompany with the following symptoms:
-Knee pain during walking, running, landing or jumping.
-Catching or locking of the knee.
-The feeling of the knee “giving away”.
-Limited range of motion/movement of the knee.
-Sensation of clicking within the knee joint during movement.
-Tenderness on the side of the knee when touched.
Treatment of meniscal injury
In general, a non-surgical healthcare profession such as chiropractic will aim to:
-Reduce pain and inflammation of the knee joint.
-Return normal knee joint movement and range of motion as promptly as possible.
-Balance muscle strength and symmetry.
-Improve patellofemoral function if required.
-Return to usual activity or sport.